After a long day away from our children, we parents are eager to hear all the details about how they have spent their time. However, so often our queries of “What did you do today?” are met with the same predictable response: “Nothing.” For children, distilling the many details and experiences of a full day at school into an anecdote or two is a tall order. What tools can we use to get them talking about their learning?
Vidigami
Through the Vidigami private photo sharing platform, you get to see moments of your child’s day at school. Viewing photos of your child engaged with Montessori materials can inspire great conversations. Children, especially those younger than five, are not yet able to summarize and describe the many things they experience over the course of a full and stimulating school day. However, photos offer visual cues that trigger a child’s memories and invite them to comment on specific materials and activities. There are many different ways to talk about these photos with your child, and we've provided some suggestions, which focus on your child's intrinsic motivation. Enjoy these special conversations as you allow them to teach you what they are learning at school.
- Ask your child to tell you about the photo. You may learn what they see in the classroom, or what they remember about the moment, and it may be much more than meets the eye.
- Say what you see without judgement. “I notice you are in the classroom.” “Do you know the name of that work?” “There are a lot of colors in your drawing.”
- Speak about their efforts instead of praising their product. “You really look like you are concentrating.” “Is that the first time you have done that work?” “I see your smile. What did you like about that work?” “Are you building with those blocks?”
Intrinsic Motivation
Listening to your child talk about the photos and speaking without judgement encourages your child's intrinsic motivation – it allows them to continue to work for their own sake, rather than for any praise from adults. As Montessori teachers, we get to witness this intrinsic motivation every day. It looks different at each age grouping and is a critical element to Montessori education. Many elements of the method foster intrinsic motivation without reward and judgement, such as control of error in the materials, allowing for repetition, assessment through observation, and relying on peers as sources of feedback and inspiration. Teachers try never to interrupt a concentrating child or judge their work. Instead, they seek opportunities for meaningful conversations before or after a student's work cycle.
As Montessori observed children, she saw time and time again the intrinsic motivation in the child to work through repetition for long, uninterrupted periods of time. In a book that examines Montessori’s relevance to today’s educational practices, "The Science Behind the Genius," Angeline Lillard refers to several current research studies confirming that rewards and punishments not only negatively impact intrinsic motivation, but also how a student performs on the task. Traditional reward methods used in most schools may actually hinder a child’s performance. Given the opportunity, children are capable of learning to take personal responsibility for their actions.
“Like others I had believed that it was necessary to encourage a child by means of some exterior reward that would flatter his baser sentiments … in order to foster in him a spirit of work and of peace. And I was astonished when I learned that a child who is permitted to educate himself really gives up these lower instincts.” – Dr. Maria Montessori
As a Montessori school, we believe deeply in educating the whole child: their academic, psychological, critical-thinking, moral, and social-emotional selves. In addition to the academic lessons and works your children are engaged in daily, our teachers and staff are also guiding your child through other very important lessons to help them with their moral and social-emotional development. For example, teachers give explicit lessons related to grace and courtesy, facilitate discussions at the peace table, and encourage collaborative work and play daily.
And, it turns out, research from our School confirms that we are doing this pretty well …
The Gratitude Project
We recently worked with Professor Jonathan Tudge and his team from the University of North Carolina at Greensboro ("UNCG") to study the development of gratitude as a virtue. As a virtue, gratitude goes beyond a positive feeling when something good happens. Virtuous gratitude is a disposition to act gratefully when someone else does something nice for you. Dr. Tudge explained it to me this way: “Saying 'thank you' is polite, but hardly a virtue. What makes gratitude a virtue is when beneficiaries of good deeds or significant help want to do something back for their benefactor if they have the chance to do so. That first act of generosity, followed by grateful reciprocity, leads to building or strengthening connections among people.”
In previous cross-cultural research, Dr. Tudge and his team found that most children develop this type of gratitude between the ages of 9 and 13, although the age differed depending on the cultural context. In their study, children in the United States developed virtuous gratitude at later ages than other cultures. Keeping this in mind, Dr. Tudge decided to target a new intervention designed to encourage the development of gratitude within adolescents.
Dr. Tudge and his team came to our School to explore this intervention. After working with our Upper School students, they stumbled upon a ‘good’ problem with their research: far more Greensboro Montessori School students exhibited virtuous gratitude than they expected. Our Upper Elementary and Junior High students expressed gratitude at much higher rates (67%) than did children in non-Montessori settings in the United States (46%). In addition, our students were almost twice as likely to express autonomous moral obligation (79%) than were children in non-Montessori schools (44%). Defined originally by Jean Piaget, autonomous moral obligation is a decision-making framework whereby moral decisions are made based on intrinsic motivations to do the right thing.
Dr. Tudge and his team were puzzled by these anomalous findings. Why did our students score higher than other American children, even when compared to other well-regarded private schools in the Greensboro area? And how are these findings related to Montessori pedagogy and culture?
Gratitude in the Montessori Classroom
In our discussions with Dr. Tudge, we discussed the way Montessori teachers prepare the environment to communicate honor, respect, and gratitude to the child. We also described the ways in which our teachers model gratitude and respect when they speak and interact with their students. In time, this becomes our students' definition of "how it's supposed to be.” In addition, we delineated how our grace and courtesy curriculum creates both a framework for community interactions and a schoolwide culture of character.
In collaboration with Dr. Tudge and his team, I presented the results from our Upper School students’ involvement with Dr. Tudge's gratitude study at the Association for Moral Education’s annual conference in Seattle, Washington.
In the presentation, we hypothesized that our students' high rates of gratitude could be due to several specific tenets of Montessori philosophy:
- Specific lessons about grace and courtesy provide explicit guidance on character development from a young age.
- Daily practice of grace and courtesy increase opportunities for proximal processes related to virtue development.
- Mixed age groupings of children may expose younger children to older children are further along in virtue development.
- Peer interactions encouraged from toddlerhood may increase opportunities for the development of mutual respect.
Dr. Tudge and his team also did some work with our Lower Elementary students. Tudge’s team again noted that so many of even these younger children (aged 6 to 9) expressed virtuous gratitude. Dr. Tudge reflected: “We think that this must say something about the character-based focus of the general Montessori curriculum, because a far greater proportion of Greensboro Montessori School children expressed gratitude than elsewhere.”

Dr. Jonathan Tudge and his team from UNCG discuss gratitude with Lower Elementary students from Greensboro Montessori School Students.
Character Education at Greensboro Montessori School
Overall, the results suggest that a Montessori environment is conducive to developing virtuous gratitude and autonomous moral obligation. These results – while surprising and interesting to the UNCG team and other researchers and educators at the Association for Moral Education conference – are not really that surprising to us. Focusing on strong character education is a key tenet of Greensboro Montessori School. A deep respect towards classmates and other people is so integral to our culture that it's not that surprising our Elementary and Junior High students authentically take their sense of gratitude to a level beyond just saying “thank you.”
We recently sat down with Upper School Faculty member, Jonathan McLean, to learn more about Greensboro Montessori School's Junior High Music Ensemble. Here's an edited transcript of our conversation.
Q: What exactly is Music Ensemble?
A: We have a lot of students who want to play a lot of different things or perform a lot of different [types] of music ... anyone from somebody taking violin, to taking piano, to taking singing lessons, to just hanging out at home banging around on the piano. To follow the child - and the best thing for each child - I've found is the Music Ensemble, which is just a big band.
Q: Is Music Ensemble part of students' regular coursework, or is it an elective?
A: The closest thing it's to is an elective. Certain people are required to be in it. If [a student is in] my Creative Labs class and they are always [applying] for positions for composers or being in the band, then yes, it's a requirement they have to be in Music Ensemble. They give up one of their independent studies, which makes it like an elective, and come in [the studio] and rehearse.
Q: How often do you rehearse?
A: One class block every week, which is an hour and fifteen minutes, which is barely enough. But it is Wednesdays. We loose [lots of Fridays and Mondays] every year for [teacher workdays] and national holidays. That's why I put it on Wednesday, so we lose fewer of them. We also have dress rehearsals and sound check rehearsals before any show, [which would] be on a Saturday or Sunday usually, or right after school.
Q: Who can participate in Music Ensemble?
A: Anybody that's already had at least a year’s worth of lessons on a instrument, because Music Ensemble is not for me to teach you how to play an instrument. Creative Labs, actually, is [when] I can spend some time showing a student some stuff about how to play an instrument and then get a student hooked up with an after-school or out-of-school teacher. [Music Ensemble] is an advanced music experience, and the student needs to have already made a commitment to learning an instrument. Vocalists are taking voice lessons, and some have also taken lessons on piano.
Q: Are your vocalists also taking voice lessons?
A: One, two, three. Three of them are. One of them is not. Two of them have taken lessons on piano and have switched to vocals. Once you learn an instrument, particularly piano (because if you go off to music school everybody has to take Piano 101, it's like English Composition 101 to be a writer), you can play pretty much anything.
Q: What is the age range of your current Music Ensemble?
A: 12 through 15, [but we currently have a guest drummer] who is in fifth grade. The [typical] grades are seventh to ninth ... I invited him [to join] for two reasons. One, he's a student of mine, and he's highly advanced for his age. He could play in any band and make money right now if he wanted to. He practices with me once per week and also at home. [Two,] all my drummers graduated. It was an advantageous moment.
Q: What is the single greatest lesson your students take away from working in Music Ensemble?
A: That’s easy. Working in a band is working in a group. When you do group projects in the classroom, how do you assess how much each person is carrying their weight if it's an outside project? We don't know how to do that right now. In class though, it's a little easier ... but in a band, if you are not carrying your weight, everybody knows it. There is no calling somebody out and being unfair and them saying, "No, I know my part." No, you don't, because we have to stop because [someone's] part is wrong, and I don't mean that in a harsh way, it's just one for one, like math. It's either right or wrong. It's either in tune, on rhythm and in the right spot, or it's not. That's the single most important lesson: you cannot hide in a group.
Q: How long have you been teaching Music Ensemble?
A: Music was one of the first things I did when I got to Greensboro Montessori School [in 2002]. The middle schoolers were revolting against the traditional class where students are learning music on recorders playing from the same book I used when I was in Junior High. You have to do something current for adolescents to get engaged. So when you immediately say the word “band,” they want to play.
Q: What have you learned teaching Music Ensemble?
A: The first lesson I learned was the drawback to individual lessons. I think that all people who [teach] individual lessons should have some sort of network where they get their students together to play in an ensemble or a band. I would get a full band together [at Greensboro Montessori School] and each student may have had 2 to 3 years of lessons on their given instrument, and we'd start the song, and we'd play through it, and it would just be cacophonous and terrible. If you just pulled [each musician] out magically and just listened to them, they would nail the song, but they had been taught in a vacuum. As long [as a student thinks they're] playing the song correctly, they're not even tuning in to the other members of the group. So that goes back to the step above learning to work in a group. One, you can tell who is not carrying their weight, but two, its awful, its not pleasant. To teach you to tune into that goes into all the other stuff about brain development and mathematics and what music does to your brain.
Q: What do students new to Music Ensemble need to learn?
A: They need to start listening to each other. It is self awareness and it's being aware of other people, and doing that thing Miles Davis said where everybody pushes and pulls each other. If somebody's lagging behind, it may be because they are having a hard time with a song, so the band has to tune into it, be a team, and slow down a little bit. You can get on them afterwards, like "why were you playing that so slow," but [during] a performance you support your team. But also, it may be, as they get the hang of it, somebody wants to pull the song back, and that sets the mood. Maybe someone wants to push it a little bit, but that's how musicians interact with each other.
Q: What is the most important thing you see your students do in Music Ensemble?
A: All the brain development that goes on after they learn the basics of working in a group, then to listen to each other, and then to get into it [with each other]. What I know as a performer and an entertainer is if you only have one person or 10000 people watching you, if the audience sees that [members of the band are] just up there doing [their] individual jobs, it's going to be apparent to the audience. And even if [the music] is in tune and played well, it doesn’t come together. There is a gestalt that happens when you are into your music, and I think thats the hardest thing to teach the kids to do, because at this age, kids get freaked out when they think people are watching them, and you know what I've learned from sports, it's not their parents watching them. It's their peers. That’s one of their biggest challenges they have - to perform. They don’t want to be awkward, they don’t want to play badly, they don’t want to seem stiff in front of their friends ... which actually, usually causes them to stiffen up.
Q: And where they are as adolescents, that’s an important factor to them, is what their peers think of them?
A: It is at the top of the list according to the best brain research and social and emotional research we have. They literally feel like they're going to die when they're not around their friends. So when their friends are in front of them, they cannot “mess up” in front of them. It's enormous pressure. That's a whole thing that doesn't even affect me. You know, I get nervous before I play, but once I start playing, I settle in. But these guys, that’s a real developmental thing for them to settle into that [and to learn to work through that pressure]. It will hopefully pay off when they get in front of people to present as an individual. Even if [these students] don't go on to be musicians, they will continue to feel comfortable ... presenting themselves, whether its for a college application, a job application, or giving a speech.
Q: As we wrap up our interview, do you have any final thoughts?
A: I am proud of fighting [for music and the arts] as an equal subject to math, science, and language, and I have teammates that have always supported me on that. Now I have a subject called Creative Labs which happens to be music, art, design, and anything like that, but that’s where the 21st century skills are going ... Every day you're getting music and every day you're getting art, which is what the [students] get here. It is equal across the board, but it does take a team that supports that and realizes that. I think that's something vitally different that we do here at Greensboro Montessori School.
Throughout the school year, the Junior High students at Greensboro Montessori School have multiple opportunities to delve into the study of economics through entrepreneurial experiences in both individual and group projects.
One project culminates in a Holiday Marketplace event that occurs annually during the second or third week of December.
Parents, students, friends and neighbors are welcome to come and shop at the 2017 Holiday Marketplace on Wednesday, Dec 13 from 9am-2pm in the gym.
The students work in small teams of two to three partners over the course of several weeks to develop a small business plan and manufacture a variety of hand-made products (art, food, clothing, gifts, etc.). These products are offered for sale to the entire community on the day of the marketplace event. The students are encouraged not only to design products that will make a profit but also products that are ethical and sustainable, benefiting the whole. This is a unique opportunity for the students to use their creativity, drive, talents, and business skills to make take home cash profits, which many use to fund their out of pocket expenses for overnight school field trips at the end of the school year.
In the Holiday Marketplace project, our young adolescents experience the true life of an emerging entrepreneur and small business owner:
- conducting research and development for their products,
- renting a booth/ retail space,
- creating a store front,
- paying utilities and taxes,
- developing marketing and customer service strategies,
- repaying their start up loans and
- calculating and equitably sharing their profit.
The "utilities, taxes and booth rental fees" that they pay are deposited into a school account that goes back into the Junior High to cover curricular and program expenses.
The Holiday Marketplace project represents just one aspect of how our students experience and study the principles and realities of economics. Another way is through their participation in a year-long micro-economy program that occurs every Friday. Unlike the marketplace project where the proceeds result in personal profit, the micro-economy program is designed so that any proceeds are reaped communally and expenditure must be decided on by the whole group. In some ways the micro-economy program is a “grown-up” version of the practical life lessons that are so effective in teaching our youngest students about respect for self, respect for the environment, and respect for the community as well as basic executive function skills.
The regular micro-economy program in the Junior High occurs in organized weekly sessions where the students experiment with practical life experiences in preparation for later life work. This emphasis on “real work,” as some would call it, is rooted in Dr. Maria Montessori’s belief that adolescents should learn about economic principles that govern production and exchange. By doing so, she proposed that adolescents would develop a deeper appreciation for available resources, the importance of hospitality, and that the work would provide a context for understanding human civilization and their role within it. This is work with the head and the hands! As part of micro-economy program, students engage in a plethora of meaningful work, which builds professionally applicable skills, encourages interdependence, and peaks intellectual curiosity.
Early in the school year, students begin the micro-economy program by preparing a resumé and applying for specific jobs. These jobs fall within three basic career areas, most of which directly relate to the operation of Maria’s Café, our commercially inspected restaurant program that serves a hot home-made lunch on Fridays. One team manages the kitchen including the menus, ingredients (both store bought and sourced from our gardens), food preparation and food service. Another team oversees the financial and marketing aspect of the micro-economy, and plans Junior High community events, outreach and fundraisers. The third team comprises a research and design lab that develops and fabricates new marketable products through use of tools and technology (3-D printer, state of the art design software, wood shop. etc.) and also produces the school’s yearbook.
This experience for our students is an example of applied learning at its best!
After two years worth of planning, design, collaboration, development and fabrication, our Junior High students will be hosting a grand opening of their newest venture, Maria's Market Farm Cart, including a special ribbon cutting ceremony with the Greensboro Chamber of Commerce. (The ceremony is being planned for early 2018. It was originally scheduled for December but was postponed due to inclement weather.) This project has been a near perfect example of how our students work together to bring an idea to life while engaging in real, purposeful work that not only stimulates their intellect but also teaches them valuable, lifelong skills in entrepreneurship and economics.
Maria’s Market Farm Cart was developed through an aspect of the Junior High Curriculum known as the Micro Economy Program. The 2017-18 school year marks the fifth year running the program as an integrated "Farm to Fork” business. At the beginning of each school year, students apply for jobs in the program based on their interests, talents, and abilities. Branches of the business include Research and Development, Design and Fabrication, Finance, Tribal Council, an on-site Restaurant, and a Farm Team. Click here to read more about the Micro Economy Program.
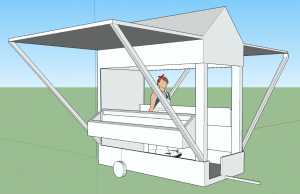
At the beginning of the 2016-17 school year, the Farm Team submitted a proposal to the Design and Fabrication Team to build a mobile market stand where produce from the School's gardens, eggs from the School’s chickens, and original student art could be sold. The Design Team jumped at the project, pledging to retrofit an old trailer bed generously donated by the School’s garden manager, Aubrey Cupit.
As the team envisioned a functional design for the mobile market stand, the team members, guided by Upper School Performance and Visual Arts Teacher Jonathan McLean, used an application called Sketchup to create the first 2D images of a mobile cart.
Student designer, Lily Wagoner, studied images, took real time measurements, and made a cut and materials list. After this thorough research phase, students began the process of building the cart. Bit by bit, the project came together with the final stages including staining and painting the cart.
Maria’s Market Farm Cart officially debuted at the 2017 Fall Festival on October 15 and has been open for business several times since then. Every Friday afternoon that Junior High has a Micro Economy day the farm cart will be open from 3:00-4:00 PM during the afternoon carline. All of the produce for sale is harvested by the students from the School's gardens. Students also make crafts and original artwork to contribute to the market, including items made by the Research and Development Team in the metal forge.

Junior High students work together to fabricate the farm cart applying principles of geometry and physics.
The Farm Cart and all of the integrated work throughout the student-run Micro Economy Program is a wonderful example of how these entrepreneurs are able to use their intellectual abilities to produce viable work that relates to real life, while simultaneously teaching them to be leaders and entrepreneurs. It also addresses the complexities of doing ethical work that benefits the community and ultimately the world. In the process, they learn the meaning and pleasure that can be derived from such work. It is what Maria Montessori envisioned for the adolescent and we couldn’t be more excited about encouraging this vital work.
“The shop would also necessitate a genuine study of commerce and exchange, of the art of ascertaining the demand and being ready to meet it, of the strict and rigid rules of bookkeeping. But the thing that is important above everything else is that the adolescent should have a life of activity and variety and that one occupation should act a “holiday” from another occupation. The shop would be in respect to the studies of economics and politics an educational object, similar to the aquarium or terrarium in the case of the study of biology.” - Maria Montessori (From Childhood to Adolescence, 70)
“Their spirit will dry up if the grandeur of the practical reality of our days is completely shut away from them, as if it did not exist. Men with hands and no head, and men with head and no hands are equally out of place in the modern community." - Maria Montessori (From Childhood to Adolescence p. 61)
In 1997, Greensboro Montessori School held its very first graduation ceremony honoring three eighth grade students. In the fall of 2017, exactly twenty years after that defining moment in the school’s history, we welcomed our inaugural 9th grade class, interestingly enough, also composed of three remarkable students: Theo Fenske, Owen Jacobs and Alex Kotis. It has been affirming to watch these boys step up to be the leaders of the student body of our school. They have each taken on the position with confidence and grace.
To support these students in their new leadership position, this year they have been meeting and interviewing local leaders in the greater Greensboro community. So far the students met with Abu Zaeem, the principal of The Newcomers School and our very own leader, Kevin Navarro, whose dissertation was written about what it means to be a vulnerable leader. Next they meet with Kevin H. Gray, the president of the Weaver Foundation.
Another important element built into our 9th grade curriculum is the completion of a year-long capstone project that challenges each student to apply his or her skills to an area of personal interest that will improve and enhance their world. Similar to a thesis or senior project, the capstone project provides a framework for demonstrating leadership and advanced application of critical thinking skills. The project is comprised of three main components: documented service learning, a written research paper, and an oral presentation, in the style of a TED talk, to the greater school community.
To further extend their learning, the students were challenged to custom design an end-of-year 9th grade field trip that would incorporate research opportunities for each of their individual capstone projects. They have been collaborating with a faculty advisor to explore a range of possibilities, and have settled on an itinerary that involves traveling throughout the Pacific Northwest. Their route will take them to explore tidal pools, tour museums in Seattle, visit a military base in Tacoma and interview refugees in Vancouver.
The three projects are as diverse as the students who developed them and include topics of refugee resettlement, marine ecology and military engineering.
In addition to making steady progress on their capstone projects, the students are taking a full academic course load which fulfills and surpasses the North Carolina state requirements for 9th grade. Their course load includes an honors level English class, an honors level biology class, an online Economics and Civics class, Math 1 or Math 2, and either Spanish 1 or Spanish 2.
So far this has been a productive, busy year for our three inaugural students. As they look ahead at matriculation into 10th grade in fall 2018, they will be well poised for any high school of their choosing whether public, private, charter or otherwise.
Their experience has paved the way for others to follow and their leadership in the realignment of the Upper School (4th-5th-6th and 7th-8th-9th) has reinforced the validity and tremendous benefits of the three-year developmental cycle.
In 2005, Greensboro Montessori School eighth graders first traveled to Costa Rica for a cultural immersion experience. We were eager to connect with another Montessori school abroad with a similar adolescent program. Our research led us to The Summit School in Coronado, Costa Rica which is very close to the capital city of San José. On our first expedition to Costa Rica, we incorporated a formal school visit to The Summit School and it was the highlight of our trip. The parents made a special lunch for us, and our students assisted the younger Costa Rican children with a school project. When we returned the following year, students from The Summit School accompanied our students in our daily travels and service learning adventures. At that point, Greensboro Montessori School and The Summit School became sister schools.
Since then, the eighth grade trip to Costa Rica has morphed into an authentic immersion experience. Our students stay with the Costa Rican families of The Summit School students, and together, our students and the Ticos (a colloquial term for natives of Costa Rica) go everywhere together. We visit volcanoes, complete high ropes courses and sail through the rainforest canopy on zip lines. We travel to the Caribbean Coast where we walk the beach at night looking for turtle eggs to bury in a nearby protected hatchery. We travel to the Pacific side to snorkel and explore rain forests and animal sanctuaries. We spend a day in downtown San José learning about Costa Rican history, art, and government. Our weekends are spent with the host families doing what they usually do. The students also do things you would expect them to do on the weekends: they get together and go to the mall or a movie or a party at someone’s home.
Every year, when asked what our students’ favorite part of the trip is, they always say their homestay with the Tico families. Our students make friendships that last for years, and some even return to Costa Rica on their own to visit their “families.”
In 2009, the Ticos first ventured to Greensboro Montessori School to stay with our students and learn more about North Carolina. Even though we don’t have erupting volcanoes or zip lines through the rain forest, we still have a great time sharing the landmarks and natural wonders of our state with them. Our visits have included such destinations as the Duke Lemur Center, the North Carolina Museum of History, and Hanging Rock State Park. On a recent visit, our itinerary included kayaking on the Dan River, exploring Grandfather Mountain, and a tour of the Duke University Marine Lab in Beaufort. Our homestay hosts always arrange social gatherings for the students on the weekends. The Ticos typically experience some classroom time with us as well as a trip to The Land in Oak Ridge.
Our students benefit tremendously from the life-changing experiences resulting from our relationship with The Summit School. With every visit to Costa Rica, our students return with their eyes a little wider and their lives a little richer as they have their first experience actually living in another culture. They begin to see the world in a different light and develop a new appreciation for the abundance in their lives.
Greensboro Montessori School sends tremendous congratulations and a fond farewell to our class of 2017. In our lead photo for this post, the class of 2017 stands proudly in the top row. Pictured from left to right are Isabel Egbert, Jean-Lou Paré, Jack Brown, Sophie Strugnell, Baxter Smelzer, Simon Smith, Eli Wainscott, Ya Chukasul, and Hayden Juneau. The inaugural ninth-grade class, who will return next year, kneels along the bottom row. Pictured from left to right are Alex Kotis, Owen Jacobs and Theo Fenske.
[dt_sc_h2] Sound Bites from the Class of 2017[/dt_sc_h2]
Greensboro Montessori School's graduation exercises include personal speeches from the graduates. In these moments, the audience is treated to glimpses of each graduate's past, present and future. In honor of these young adults' self-awareness, maturity, accomplishments and gratitude, we share some of the most touching thoughts shared by the class of 2017. Photos courtesy of Aris Wells Photography
[dt_sc_h5]Jack Brown[/dt_sc_h5]

"I have only been at Montessori for three years, but I have gotten the experience of a lifetime. I can say, without a doubt, that this Montessori experience will put me ahead all throughout my life. First of all, I'd like to thank my parents for sending me to this school...Like all things in life, things come and go away, sometimes even too quickly. And when I found my grade the oldest one in Montessori, I knew it had been too quick. Although I have been dreading leaving this school, I am also looking forward to the upcoming year."
Jack's next stop: Grimsley High School
[dt_sc_h5]Ya Chukasul[/dt_sc_h5]
 "Now Middle School. Nothing has changed a lot about me; I'm still quiet as I could ever be. Old friends were still there for me, so I felt safe. Things changed here though. Assignments got more difficult and [there were] projects I thought I would never be able to do. From creating a wolf suit on stilts, to creating costumes, to creating a movie. Teachers in Middle School: Jonathan, Doug, Deirdre, Dean, Jenny, Sandra, Matt and Keisha. Without your help, I wouldn't be on this stage today. Middle School felt just like family."
"Now Middle School. Nothing has changed a lot about me; I'm still quiet as I could ever be. Old friends were still there for me, so I felt safe. Things changed here though. Assignments got more difficult and [there were] projects I thought I would never be able to do. From creating a wolf suit on stilts, to creating costumes, to creating a movie. Teachers in Middle School: Jonathan, Doug, Deirdre, Dean, Jenny, Sandra, Matt and Keisha. Without your help, I wouldn't be on this stage today. Middle School felt just like family."
Ya's next stop: Weaver Academy for the Performing and Visual Arts and Advanced Technology
[dt_sc_h5]Isabel Egbert[/dt_sc_h5]

"Before I do anything, I need to thank my family. Grant, you made me who I am in ways you can't even understand. You are always there for me, and I love you. Mom and Dad, thank you for putting me in this school and for supporting me in everything I do...Eighth grade is a confusing, scary fever dream. Everything stops being just a thing and becomes your last thing. Your last Marketplace; your last Land trip; your last Advisory; [your] last time in CASA; until finally, you're standing here for the last time. Thank you all for everything."
Isabel's next stop: Weaver Academy for the Performing and Visual Arts and Advanced Technology
[dt_sc_h5]Hayden Juneau[/dt_sc_h5]

"In his final year at this school, this kid, alongside his partner in crime, Owen Jacobs...started to run everything tech related, doing things like being the first students to run [theatrical productions] by themselves. This kid, in his final year, found out what he wanted to be. He found out what he was skilled at, and here he is, standing on a stage, the last day he will be a student here, telling you about the last three years of his life in the third person. How - meta - is - that?"
Hayden's next stop: Weaver Academy for the Performing and Visual Arts and Advanced Technology
[dt_sc_h5]Jean-Lou Paré[/dt_sc_h5]

"It took a little bit of time to adjust to the new homework load, but once I got past that, I had lots of fun in Jonathan's long-term [creative labs] projects, Dean's science labs, and Doug's math classes. I also had a blast at the land helping the Racoon tribe set up the Tipi, make a fire, and the fun job of washing dishes. I also enjoyed the woodworking rotation...Thank you to everyone that has helped make my experience at GMS the best it could be and making it possible for me to attend the STEM Early College next year."
Jean-Lou's next stop: STEM Early College at NC A&T State University
[dt_sc_h5]Baxter Smelzer[/dt_sc_h5]
"After 12 years of the Greensboro Montessori School, I am definitely going to miss it. Leaving can be a scary and an exciting time. And I have had not only amazing relationships with friends throughout the years, but also with the teachers. You couldn't ask for more involved and caring teachers. Teachers, staff, and friends all in [an] awesome Montessori environment that all helped me grow to be ready for the next step in my life. After being here, I look around and realize I am ready. I have been well prepared and have learned the skills I need to move forward."
Baxter's next stop: Page High School (pre-IB) or Weaver Academy for the Performing and Visual Arts and Advanced Technology
[dt_sc_h5]Simon Smith[/dt_sc_h5]

"I have spent..12 years of my life in this school and sometimes I gotta ask, 'Is this the real life or is [it] just fantasy?' This school has been amazing to me from the teachers to the staff, and this place has most definitely given me its all...A little known fact about me..I don't like change. But life forces you to change whether you like it or not...You just have to adapt."
Simon's next stop: Weaver Academy for the Performing and Visual Arts and Advanced Technology
[dt_sc_h5]Sophie Strugnell[/dt_sc_h5]

"My experience at GMS has definitely been special...Learning in [a] Montessori environment is a lot more free. There aren't as many guidelines, and it's more based around genuine curiosity. I think in Montessori there are a lot more lessons that are being learned, and there are a lot of life skills that are involved. I've really enjoyed my time here and have made many memories with many people. Even though I've only been here one year, I'm gonna miss everyone so much, but I'm excited to see what's in store for me next."
Sophie's next stop: Northern Guilford High School
[dt_sc_h5]Eli Wainscott[/dt_sc_h5]
"My final word describes my Middle School experience is 'nuevo,' which means 'new' in Spanish. Everything is new here. You are thrust into projects and situations that you've never experienced before, and it's blissfully confusing to figure it out, solve the puzzle, get rid of the grit on the lens to see the full picture. I've done it all now, however. I've planted microgreens; I've led a group to be saved by aliens; I've branched out to new people, new groups of people; and I've learned by this. By every moment, every decision, I've grown as a person."
Eli's next stop: Weaver Academy for the Performing and Visual Arts and Advanced Technology
<hr>
[dt_sc_h2]Looking Ahead to the Class of 2018[/dt_sc_h2]
In 1997, Greensboro Montessori School graduated its first class of three eighth-grade students. It seems fitting on the 20th anniversary of that historic occasion, we are proudly introducing the School's first class of ninth-grade students, and it is also comprised of three students. Greensboro Montessori School is proud to announce the intelligent, talented, creative and courageous young men who are boldly pioneering the School's ninth-grade program.

Theo Fenske

Owen Jacobs

Alex Kotis
We recently began a discussion on the quintessential similarities between computational thinking and the Montessori method. The three-part blog series is inspired by a recent New York Times article by Laura Pappano entitled “Learning to Think Like a Computer.” In our first post, we explained how even the simplest of Montessori materials teaches computational thinking skills. In this second installment, we highlight how the Montessori approach to education develops computational thinking within students.
We met with Jonathan McLean to talk about his semester-long assignment in the Middle School’s Creative Labs course. Like all classes in the Montessori curriculum, this visual and performing arts class integrates subject matter from other areas of study. More specifically, Jonathan is weaving together STEM (Science, Technology Engineering and Math) and Art History through a complex science fiction role-playing game involving student-built robots and drones. To make sense of the story and succeed in the game, Jonathan’s students must employ computational thinking skills.
Just what are these skills? In her New York Times article, Laura Papanno says they are “recognizing patterns and sequences, creating algorithms, devising tests for finding and fixing errors, reducing the general to the precise and expanding the precise to the general.”
Our middle school students are flexing all these mental muscles in a battle royale between the Drones and the Bots, the only remaining cultures in the elaborate story guiding this semester’s coursework. The setting is such: The Earth has overheated making it inhabitable for organic life. Only two warring cultures, Bots and Drones remain, but neither are safe. Volcanic activity threatens the Bots on land and atmospheric change jeopardizes the Drones in air. The Bots and Drones must appeal to an Alien culture to save them, and it just so happens the Aliens have tremendous reverence for the visual arts. As the Bots and Drones compete for the Aliens’ benevolence, they must do so with aesthetically appealing design and decoration which aligns with the Aliens’ favorite artistic movements.
As the facilitator, Jonathan plays the role of the Alien culture. The students are divided into multi-age teams aligned with either the Bot or Drone culture. Jonathan gives the students data sets with which to design, build and operate their Bots and Drones. The teams consist of students in the various rolls such as officer, designer, engineer and pilot. As the students receive, process and make sense of the data they receive, they must adapt to survive. Whether either or both cultures escape the Earth will be determined in a three-hour Bot versus Drone showdown next week. The teams’ performances are the students’ final exam for the class (and Jonathan has a surprise finale planned for the students if they find a win-win solution for the Bots and the Drones).
Rather than dictate or force rote memorization upon their students, Montessori teachers educate through integrated experiences. Jonathan has created a fictional and engaging theme to provide a framework in which the students are able to apply real-world skills. Students are absorbing data from multiple sources to identify problems, understand the scope of the problems and develop and test solutions. Additionally, Jonathan is purposefully withholding information forcing the students to uncover new information and draw conclusion on their own. Harkening back to Laura Pappano’s words about computational thinking: “Concealing layers of information makes it possible to get at the intersections of things, improving aspects of a complicated system without understanding and grappling with each part. Abstraction allows advances without redesigning from scratch.”
If all of this sounds like a lot of fun, it is. Our middle school students are learning science, technology, engineering and math in their visual and performing arts class. If a student loves art, he can pursue this interest through the final appearance of his Drone, but he must also ensure aesthetic enhancement doesn’t impact physical performance. On the contrary, if a student loves engineering, she can fuel her curiosity through building her Bot, but the structure must accommodate one of the Aliens’ preferred art movements, for instance, Cubism.
In most schools throughout the country, these two students couldn’t thrive in the same class, but the Montessori method demands they both succeed by allowing them to pursue their passions through integrated curriculum and independent study. No single class takes place in a vacuum of learning, and students must carry their knowledge and experiences from one class to another. Ultimately, it’s learning how to think (like computational thinking skills), versus what to think which prepares these students for a lifetime of achievement.
As people learn that Greensboro Montessori School will offer ninth grade beginning in 2017, they ask, “Why are you offering ninth grade? Aren’t your students ready for high school?”
The fact is, our graduates are more than ready for high school. Our middle school program is highly effective at preparing students for a lifetime of achievement, and the qualities of our program look exactly like the middle school described by Dr. William M. Alexander (1912–1996). Alexander, who is widely recognized as the “father” of the American middle school movement, said good middle-level schools (called junior high schools at the time) offered “more of the freedom of movement they need, more appropriate health and physical education, more chances to participate in planning and managing their own activities, more resources for help on their problems of growing up, and more opportunities to explore new interests and to develop new aspirations.”1
Therefore, the question should not be whether Greensboro Montessori School’s middle school is effective. Instead, it should be, “How effective is ninth grade in high school?” Data and educational trends indicate that today’s high school fails to meet the developmental needs of the ninth-grade student.
“Ninth Grade: The Most Important Year in High School” was published on November 1, 2013 on The Atlantic’s website. It’s premise flows from recent research that finds “ninth graders have the lowest grade point average, the most missed classes, the majority of failing grades, and more misbehavior referrals than any other high-school grade level.” The article’s author, Michele Willens, writes, “Not only are youths entering the intimidating institution that is high school, they are experiencing the usual adolescent angst and depending on poor decision-making skills. ‘Students entering high school—just at the time brains are in flux—still have the propensity to be impulsive and are prone to making mistakes,’ says Washington D.C. psychoanalyst Dr. Linda Stern. ‘They are therefore experimental and trying to separate…Put all that together with raging hormones, the normal academic pressures, and meeting a whole new group to be judged by.’”
A blog from Public School Review further explores how the traditional ninth-grade setting impacts adolescents and how “many schools are restructuring their programs so that ninth graders are in a separate setting, apart from the larger high school community.” This trend has taken hold to serve ninth graders’ “distinct needs,” and researchers at Boston College have already determined the effectiveness of the model. “Results from the study show that, overall, the isolation of ninth graders in ‘a separate building, wing or floor eases the transition to high school.’ Paired with this, ‘Ninth grade students benefit by building relationships with peers in the same grade,’ as students, teachers, and [administrators] reported fewer concerns of bullying by older students.”
As Montessorians, when we combine this research with our own knowledge of Dr. Maria Montessori’s four phases of development, we proclaim with certainty that offering ninth grade is the right thing to do for students and their families.
During her groundbreaking studies, Dr. Montessori defined four phases of development in a child’s journey to adulthood: the absorbent mind from zero to six; childhood from six to 12; adolescence from 12 to 18; and the young adult from 18 to 24. Within each phase, Dr. Montessori uncovered two distinct, three-year learning cycles (or subphases) based on sensitive periods of growth and development shared among the age group. The three-year cycle results in multiage classrooms where skills and concepts are introduced, explored and mastered through consecutive years of learning. The three-year cycle also reinforces student leadership through social development.
The adolescent phase of development is unique. Dr. Montessori said, “The third period goes from 12 to 18, and it is a period of so much change as to remind one of the first [period from ages zero to six]. It can again be divided into two subphases: one from 12 to 15, and the other from 15 to 18. There are physical changes also during this period, the body reaching its full maturity."2
The first adolescent subphase from 12 to 15 equates to seventh, eighth and ninth grades. Dr. Montessori would advocate that ninth graders – based on their collective social, emotional, mental and physical development – should be leaders in a multiage grouping with seventh and eighth graders. She would further argue their minds and bodies are better served when positioned as mentors.
Graduates of Greensboro Montessori School thrive in four-year high schools. We count multiple valedictorians, salutatorians and Morehead Scholars among our alumni, and we know some students will continue to graduate in eighth grade and matriculate beautifully into private and public high schools. But Dr. Montessori’s developmental phases and today’s educational research also tell us high school isn’t meeting the needs of ninth graders. As a member of the Greensboro community, leaders in the field of education, and stewards of our students’ education, we have an obligation to offer ninth grade. Not because we think students will have a poor experience elsewhere, but because they will be better served by the ninth-grade experience at Greensboro Montessori School.
1Alexander, William M. “The Junior High School: A Changing View.” Tenth Annual Conference for School Administrators: A National Conference on the Junior High School, July, 1963. Cornell University, Ithaca, NY. Keynote Address.
2Montessori, Maria. The Absorbent Mind. 1949.